Researchers at the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (Empa) have invented a new material. It combines biodegradability, strength, and versatility – a challenge that materials scientists consider far from simple.
Researchers processed the fibers. mycelium the common split gill mushroom (Schizophyllum commune) into a liquid mixture, without killing them or disrupting their natural biological functions.
The gel-like material obtained by the team was named living fibrous dispersions: LFD. It can be shaped into various forms. It also fully utilizes the substances produced by fungi.
« Mushroom “This extracellular matrix is used to gain structural and other functional properties,” noted materials scientist Ashutosh Sinha. In their work, the team utilized this feature of the cleavage of ordinary materials, the publication reported. Science Alert .
By developing a certain strain, researchers stimulated the growth of two molecules: the polysaccharide schizoheptan and hydrophobin. They play a crucial role in giving LFD its appealing characteristics.
What else is known about the new material?
Scientists also reported that they managed to create a thin film from LFD with very high tensile strength. It can be used to produce bags that will decompose naturally or biodegradable batteries.
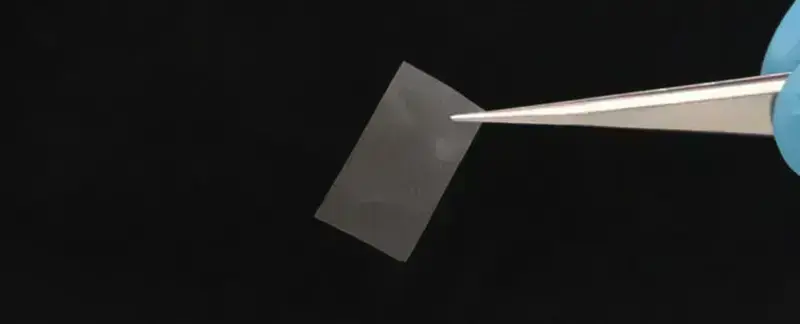
LFD is also a good emulsifier – a substance without which other materials cannot mix and bind. This emulsifier can be used in the production of food products and cosmetics: from ice cream to shampoo.
Since the mycelium of the fungus in the newly created material is alive, it continues to release more and more of its key molecules. “This is probably the only type of emulsion that becomes more stable over time,” said Sinha.
Since LFD is derived from an edible mushroom, the material is completely non-toxic and can even be eaten.
The creation of such material is extremely relevant for humanity, which is struggling with plastic pollution .
Researchers hope to find more practical applications for their invention over time, which was inspired by nature. In this way, the scientists have once again demonstrated that the natural world is the best laboratory.
The results of the study were published in the journal Advanced Materials.
