The future is arriving faster than we think. What recently seemed like science fiction is now a reality. Scientists tend to believe that the latest technologies of the future will change the way we live and help prevent a climate catastrophe.
AI is already writing poetry and creating images, 3D printers are producing implants, laboratories are growing artificial food, and robots can read thoughts. However, this is just a part of what the most fascinating technologies of the future can offer to the world.
Necrobotics
As noted by the publication Sciencefocus This technology of the future involves transforming dead organisms into robots. It sounds eerie. However, a team of researchers has already managed to turn a dead spider into a robot capable of picking up other objects. Currently, the concept is in the development stage, but in the future, scientists will be able to use dead animals for scientific advancement.
Sand batteries
Finnish engineers have found a way to turn sand into a giant battery. Tons of sand in a steel container were heated using wind and solar energy. The heat generated was distributed to provide energy for nearby buildings. This could potentially become another unconventional energy source in the future.
Electronic skin
Engineers have developed a wireless soft electronic skin that could make internet hugs a reality. It is equipped with flexible actuators that detect the user’s movements and convert them into electrical signals. These signals can be sent to another system of such a device via Bluetooth, where the actuators convert them into mechanical vibrations that mimic the original movements.
VR with a sense of smells
Researchers have recently invented virtual reality (VR) applications that allow users to experience smells. One version of this device can be “attached” to a person’s upper lip for easy access to the nostrils.

Another design resembles a mask with hundreds of different scent combinations. Scientists note that this cutting-edge technology has a wide range of applications – from online learning to watching 4D movies.
Catapulting satellites into space
NASA is already testing SpimLaunch – a prototype of a satellite delivery system that uses kinetic energy instead of conventional chemical fuel technology. With this future technology, payloads can be spun at speeds of 8000 km/h and then launched into the sky through a large launch tube. Scientists claim that this system reduces fuel and infrastructure use by 70%.
Xenotransplantation
Scientists believe that the procedure of transplanting, implanting, or infusing animal-derived cells, tissues, or organs into humans has the potential to revolutionize surgery. Currently, one of the most well-known such procedures is the transplantation of a pig heart into a human. These operations are risky at the moment, but in the near future, xenotransplantation could occur on a regular basis.
AI image generation

Illustration created by a neural network.
AI is already capable of creating images based on formulated prompts. Just enter a description, and you can receive a multitude of entirely original images that correspond to it. In the future, these technologies could be used to create art exhibitions and quickly generate original illustrations.
Mind-reading robots
Brain-reading technologies are no longer science fiction. Researchers have developed a means for patients who cannot move their upper or lower limbs to interact with the world.
According to scientists, the algorithm embedded in it can be adapted to individual preferences and brain signals. For example, in the future, there may be wheelchairs controlled by the brain.
3 D- printed bones
3D printing will allow us to create anything – from building houses to sturdy armor. However, the most interesting application is the creation of 3D-printed bones.
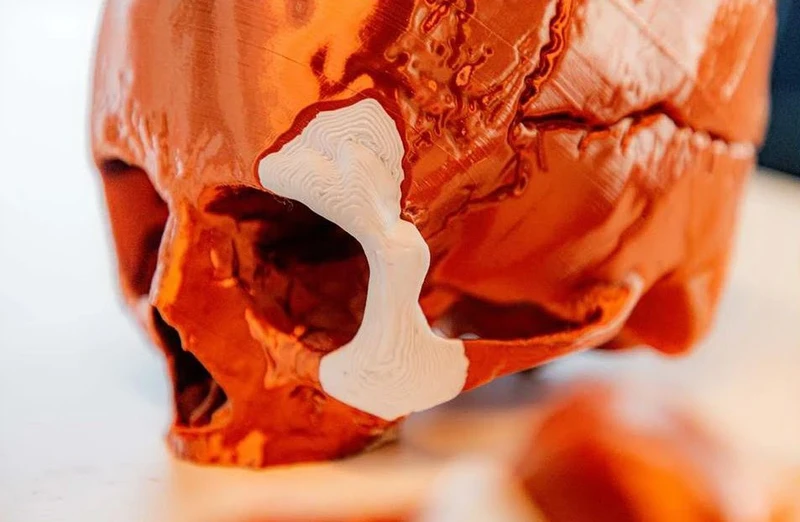
The surgeon accepts the design, and then, when the implant is printed, it can be used in surgery. Due to the use of tricalcium phosphate – a material whose properties are similar to human bones, 3D implants will allow for the complete restoration of the function of the bone they replace.
3 D- printed food
There is already a device that can create a cheesecake using seven ingredients with food inks and then cook it to perfection using a laser. This technology could be used in the future to create personalized dishes for everyone.
Natural language processing
The company OpenAI has created the chatbot ChatGPT, which can write poems from scratch, easily explain complex theories, and engage in full conversations just like a human. Currently, it is the most striking example of AI and its future. It can create entirely new websites from scratch, write entire books, and even make a few jokes.
Digital twins for health monitoring
An American company has developed a scanner that will measure hundreds of biomarkers in about an hour: from hormone levels to fat accumulation in the liver and even inflammation markers. cancer .

This data will be used to create a digital twin – a three-dimensional avatar of the patient’s body. It can be tracked over time and updated with each new scan.
The technology of the future for carbon capture.
The cutting-edge DAC technology will replace the role of trees in absorbing carbon from the atmosphere. It involves extracting CO2 from the air and storing it in deep geological caves underground or using it in combination with hydrogen to produce synthetic fuel. For now, this technology requires further refinement, but in the future, it could become one of the best technological achievements for the environment.
Energy-saving bricks
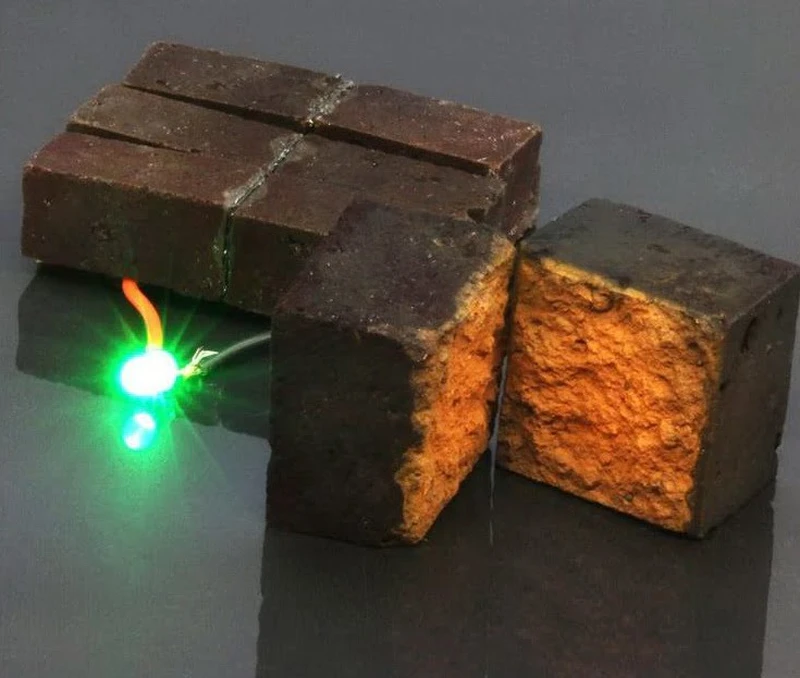
Researchers have developed a method to transform red bricks into battery-like structures. A conductive coating was applied to the brick samples, which then soaked through the porous structure of the fired bricks, turning them into “energy-storing electrodes.” According to the scientists, walls made from these bricks “can store a significant amount of energy” and “can be recharged hundreds of thousands of times within an hour.”
Self-healing “living concrete”
Scientists have created an innovative material using sand, gel, and bacteria Researchers claim that this building material has a structural support function, is capable of self-healing, and is more environmentally friendly than real concrete. In their opinion, this technology paves the way for future building structures that could “heal their own cracks, absorb harmful toxins from the air, or even glow on command.”
Fuel from air
Swiss chemical engineers have created a prototype device that can produce hydrogen fuel from water present in the air. It uses semiconductor materials that collect energy They harness sunlight and use it to produce hydrogen from water molecules present in the atmosphere. The gas can then potentially be converted for use as a liquid fuel.
Internet for everyone

The company Hiber is launching its own network of microsatellites the size of a shoebox into low Earth orbit. They activate a modem connected to your computer or device as they fly by and deliver data. Hiber satellites orbit the Earth 16 times a day and are already being used to provide internet access in very remote corners of the planet.
3 D- printed eye tissue
American researchers have created retinal tissue using stem cells and 3D bioprinting. This future technology could allow scientists to model the human eye to better understand and develop treatments for diseases that affect vision.
Car batteries that charge in 10 minutes
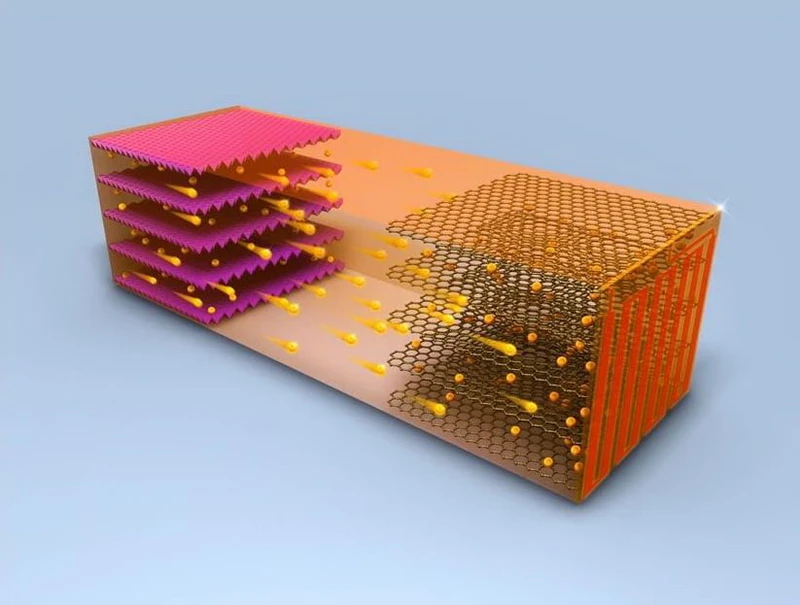
The battery design developed by American researchers self-heats through a thin nickel foil. The foil creates an electric circuit that heats up in less than 30 seconds to warm the inside of the battery. This allows for a full charge of an electric vehicle in just 10 minutes.
Artificial neurons on silicon chips
Scientists have found a way to connect artificial neurons to silicon chips, mimicking the neurons of our nervous system and replicating their electrical properties. These neurons require only 140 nanowatts of energy. Researchers hope that their work can be used in medical implants for treating heart failure and Alzheimer’s disease.
sciencefocus.com
